Mastering Secure Shell (SSH) For Remote IoT Device Management
Secure Shell (SSH) is a critical tool for securely managing remote devices, particularly within the expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. As IoT devices grow in number and complexity, understanding SSH's role in remote management becomes indispensable. This comprehensive tutorial will guide you step-by-step through setting up and utilizing SSH for efficient and secure IoT device management.
In today's highly interconnected world, IoT devices are integral across numerous industries, from smart homes to advanced industrial automation systems. However, ensuring the security of these devices remains a top priority. SSH offers a secure channel for remote access and management, safeguarding sensitive data and operations from unauthorized intrusion.
This SSH RemoteIoT tutorial caters to both beginners and advanced users. Whether you're initiating your first IoT project or looking to refine your current setup, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary for secure and efficient device management.
Read also:Alexis Bellino Net Worth 2023 A Deep Dive Into Her Wealth Career And Lifestyle
Contents Overview
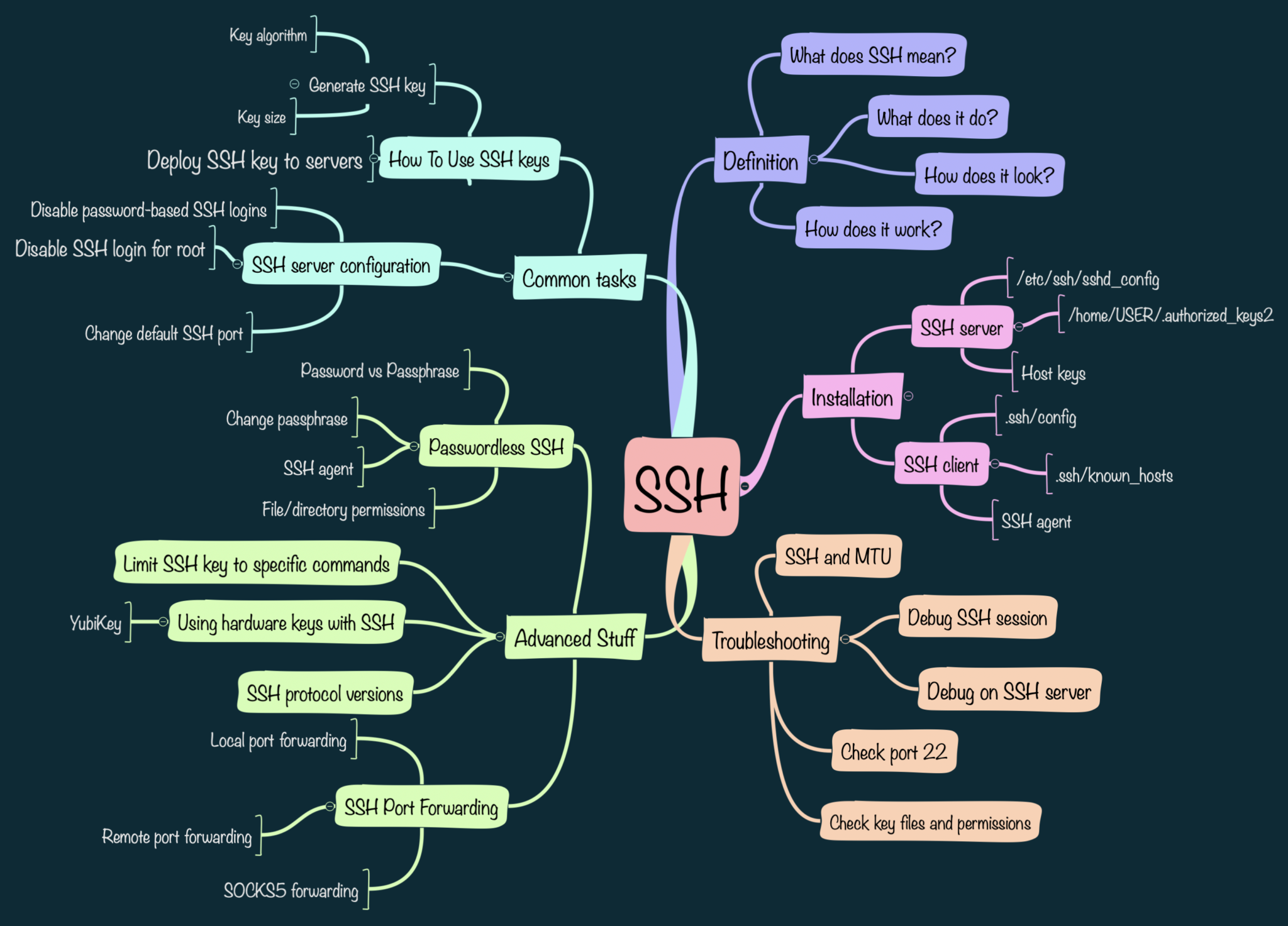
The Importance of SSH in RemoteIoT
Configuring SSH for IoT Devices
Establishing Connections to RemoteIoT Devices
Fortifying Your SSH Connection
Read also:Discover The Enchanting Beauty Of Inka Terra In Stony Point
Exploring Advanced SSH Features
Best Practices for RemoteIoT Management
Practical Use Cases for SSH in IoT
Understanding SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol designed for secure communication between devices over potentially insecure networks. It enables users to access remote devices and execute commands with high levels of security. SSH plays a pivotal role in IoT environments by facilitating remote device management while ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
SSH operates on port 22 by default, utilizing encryption algorithms to safeguard data transmission between the client and server. Its core features include robust authentication, encryption, and integrity verification, making it indispensable for remote device management. Key advantages of using SSH include:
- Secure communication even on untrusted networks
- Strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access
- Protection against data tampering and interception
- Support for secure file transfers via SFTP
The Importance of SSH in RemoteIoT
IoT devices often operate in locations where physical access is limited or impractical. SSH provides a reliable and secure solution for managing these devices remotely, ensuring both security and operational efficiency. By leveraging SSH for RemoteIoT, you gain the ability to:
- Access and manage devices securely from any location
- Execute commands and scripts remotely with ease
- Transfer files securely using the SFTP protocol
- Monitor device performance and troubleshoot issues effectively
SSH's robust security features make it an ideal choice for IoT applications, safeguarding sensitive data and operations from unauthorized access.
Configuring SSH for IoT Devices
Installing SSH on Your IoT Device
Before utilizing SSH for RemoteIoT, ensure that SSH is installed on your IoT device. Many Linux-based IoT devices come with SSH pre-installed; however, if it's not available, you can install it using the following commands:
For Debian-based systems:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
For Red Hat-based systems:
sudo yum install openssh-server
After installation, start the SSH service and enable it to launch on boot:
sudo systemctl start ssh
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Customizing SSH Configuration
Once SSH is installed, you can tailor its settings by editing the SSH configuration file located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Key settings to consider include:
- Port: Alter the default port (22) to a custom port for enhanced security
- PasswordAuthentication: Disable password authentication to mitigate brute-force attacks
- PermitRootLogin: Disable root login to improve security
- PubkeyAuthentication: Enable public key authentication for secure access
After making adjustments, restart the SSH service for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Establishing Connections to RemoteIoT Devices
Once SSH is properly configured on your IoT device, you can establish a connection using an SSH client. Popular SSH clients include:
- OpenSSH (command-line tool)
- PuTTY (Windows-based GUI tool)
- SSH.NET (library for .NET applications)
To connect via OpenSSH, use the following command:
ssh username@ip_address
Replace "username" with the IoT device's username and "ip_address" with its IP address. If you've modified the default SSH port, include it in the command:
ssh -p custom_port username@ip_address
Fortifying Your SSH Connection
Implementing Public Key Authentication
Public key authentication is a secure method for verifying SSH connections without relying on passwords. To set it up:
- Generate a key pair on your local machine:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
- Transfer the public key to your IoT device:
ssh-copy-id username@ip_address
With this setup, you can now connect to your IoT device without entering a password.
Disabling Password Authentication
To further enhance security, disable password authentication in the SSH configuration file:
PasswordAuthentication no
Restart the SSH service after making this change.
Addressing Common Issues
While using SSH for RemoteIoT, you may encounter some common challenges. Below are solutions to help resolve them:
- Connection Refused: Verify that the SSH service is operational and the firewall permits connections on the specified port.
- Permission Denied: Confirm the correct username and IP address are used, and review the SSH configuration for authentication settings.
- Timeout Errors: Assess the network connection and ensure the device is accessible.
If issues persist, consult the SSH logs for additional insights:
sudo journalctl -u ssh
Exploring Advanced SSH Features
Tunneling with SSH
SSH tunneling enables the secure forwarding of network traffic between devices. This is especially beneficial for accessing services running on your IoT device from a remote location. To establish an SSH tunnel:
ssh -L local_port:destination_host:destination_port username@ip_address
This command forwards traffic from the specified local port to the destination host and port on the IoT device.
SSH Port Forwarding
SSH port forwarding allows you to access services running on your IoT device through a secure SSH connection. There are two types of port forwarding:
- Local port forwarding: Forwards traffic from your local machine to the IoT device.
- Remote port forwarding: Forwards traffic from the IoT device to your local machine.
Best Practices for RemoteIoT Management
When using SSH for RemoteIoT, adhere to these best practices to ensure security and efficiency:
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Regularly update your IoT devices and SSH software to address vulnerabilities.
- Monitor SSH logs for any suspicious activity.
- Restrict SSH access to trusted IP addresses using firewall rules.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your IoT devices effectively.
Practical Use Cases for SSH in IoT
SSH finds numerous applications in IoT environments, such as:
- Remote configuration and management of IoT devices
- Secure file transfers between devices using SFTP
- Monitoring device performance and troubleshooting issues
- Executing scripts and commands remotely for automation purposes
These use cases highlight the versatility and significance of SSH in IoT ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
This SSH RemoteIoT tutorial has provided a comprehensive overview of using SSH for secure remote device management in IoT environments. From configuring SSH to securing connections and exploring advanced features, you now possess the knowledge and tools to manage your IoT devices effectively.
We encourage you to implement the best practices outlined in this guide and explore the diverse use cases for SSH in IoT. If you have any questions or feedback, please leave a comment below. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may find it valuable. For more detailed information, explore our additional tutorials on IoT security and management.
Sources: